Everything you need to know about joints – its causes, signs, breeds and diagnostic methods – will help detect disease in the early stages. An effective treatment will help you get rid of this disease. Arthritis is a characteristic of people over 40 years old. But impartial statistics show that in recent decades, the trend of rejuvenation and women aged 30-35 has begun to suffer losses.
What is arthritis?
Arthritis is a chronic joint disease accompanied by pathological changes in hyacinth cartilage, followed by adjacent tissues, joint capsules, and synovial shells. Failure is inherently malnutrition and degenerative, which leads to changes in joint tissue structure, i. e. loss of its function. According to the same statistics, arthritis accounts for 12% of the total planet's population. 62% to 65% of all attacks of the disease fall on people over the age of 60. Among patients aged 40-60, another 30-35% of combined impairment cases are cases of this pathology. About 3% are young people aged 20-40.
The danger of joint disease shows that it is not actually completely cured. Although it helps preserve the function of the joint when it advances early in the diagnosis of pathology.
In most cases, cases of arthritis lesions in this joint are diagnosed:
- wrist joint;
- Cervical and lumbar vertebrae;
- knee joint;
- hip joint;
- Shoulder joint
- ankle joint;
- metatrangeal joints.
This disease is a characteristic of the female population - a representative of half of the female population suffers from this pathology at an older age. The joint joints in women occur at 10 times the frequency, while the male population is 10 times higher.
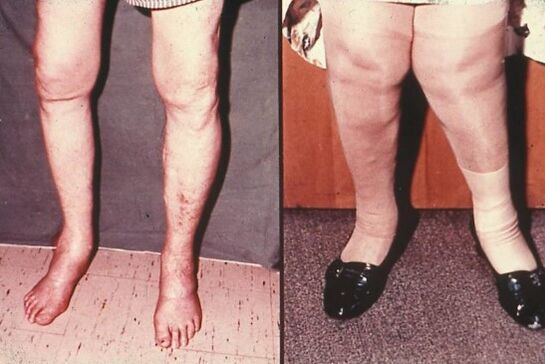
Possible consequences of joints
Through timely treatment, the disease has a less developmental intensity, thus stopping the degenerative and malnutritional changes. This means timely surgical or therapeutic intervention allows you to maintain the function of your joints, normal gait and eliminate soreness.
At the same time, tightening by treatment can lead to frequent and stable pain, laxative, joint swelling. Gradually progressive pathological changes in the tissue deprive the joint of routine function. In a short period of time, in the absence of qualified treatment, arthritis will soon flow into the chronic form. This consequence leads to the need for ongoing medical observation and regular treatment of the disease during the aggravation period.
To avoid initially suspicion of the consequences and complications of its development, you should contact a medical expert. In the early stages of joint treatment, rheumatologists engage in treatment. In a chronic form, the treatment of this pathology is performed by orthopedic trauma scientists.
Types of joints
The pathology of this joint can vary in several forms and varieties of these criteria:
- cause (main and secondary forms);
- Arthritis stage (three stages in classification);
- localization of pathology (disease manifestations and joint types);
- Localized forms (generalized and local forms);
- The course of the disease (acute or chronic).
In the symptoms, hips, knees, cystics, elbows, shoulders, ankles, and cervical arthritis.
The pathology of the main nature is classified, has no prerequisites, and is a secondary disease according to the etiology. In the latter case, joint damage is the result of the development of infectious diseases in adjacent tissues, mechanical diseases, loss of physiological function of the joints, and progressive inflammatory processes, hypothermia, injury or other factors.
Classification of positioning forms involves local and generalized damage to the joints. In the first case, the disease and its symptoms cover a small portion of the joint or its individual tissue as well as the components. With a generalized form, several joints are affected, or one of them has the effect of covering all joint tissues.
Different levels of intensity are reflected in different stages of disease progression. Meanwhile, symptoms and complications can be expressed brighter, more or less dynamically leaked fabric damage processes and impaired joint function.
According to the process of the joint, they distinguished:
- Acute shape;
- Chronic form.
Acute forms are usually manifested by an increase in the intensity of symptoms and their severity. The pain feels stronger and the morphological changes in the tissue proceed more dynamically. In a chronic form, the course of the disease is slow, manifested by individual signs during the aggravation period, and is actually not cured.
Disease degree
During the disease, the drug distinguishes three stages that vary in the intensity of the disease signs, damage and localization. Meanwhile, distinction at all three stages is related to the type of fabric that suffers from pathological changes.
- The first development of joint articulation is the initial stage of the disease. It is characterized by minor lesions in cartilage tissue and loss of physiological function in collagen fibers. Meanwhile, in the first stage, smaller morphological diseases of bone tissue and structural changes in synovial fluid were noted. The cartilage of the joint is covered with cracks and the patient has mild pain in the pathologically located position.
- The second degree is that dynamics increase joint development. This stage is characterized by stabilization of pain, color. Noting the famous morphology of cartilage and malnutrition cartridges, bone growth revealed during diagnosis. Bone-forming plants - bone growth visible in visual examination of damaged sites. At the same time, a degenerative change process of the bursa occurs, resulting in its structural exhaustion. The disease at this stage is usually aggravated and regular. The pain gradually becomes constant.
- The third degree is the active process. At this stage, the sliding fluid is almost completely absent due to its denaturation, and the bone tissues are suddenly abruptly to each other. Joint mobility is almost completely absent, and the pain becomes more realistic. There is no cartilage tissue due to degenerate and atrophic changes. Third-degree treatment of joints is considered impractical.
In addition to the development of these three pathology, all articular tissue has a final stage – irrevocable destruction. At this stage, not only is the need to perform production therapy, but it is also impossible to eliminate pain syndrome.
The inflammatory process usually begins in the second phase, and in rare cases, the inflammatory process begins without medical intervention. Subsequently, it becomes more difficult to prevent it, which may lead to the development of secondary pathology, i. e. , the pathogenic population located in the disease.
To rule out serious consequences, treatment should be initiated from level one and intensive care methods should be used. In the final stages associated with complete destruction of cartilage tissue, only one way to ride the patient out of pain and joint pain - the endohost plant can completely or partially replace the joint components.
Causes of the disease
Causes may be major and minor factors. In older people, this disease can occur through a mixture of etiologies, i. e. in the presence of primary and secondary causes. Their complex manifestations exacerbate the process of the joint and reduce the dynamics of recovery.
The main reason for most types of this pathology is metabolism violations. Changed metabolic processes lead to abnormal morphology of cartilage and synovial fluid. Therefore, these changes are associated with the entire joint and are often accompanied by the origin of inflammatory local focus.
In addition to metabolic pathology, the causes of joint arthritis are:
- Traumatic damage to individual tissues or entire joints. This includes dislocation, cracks, ligaments, meniscus rupture, penetration of wounds. This reason is more common in people participating in sports or activities related to dangerous working conditions and physical efforts;
- The inflammatory process is usually a secondary cause. Inflammation is usually found in patients with gout, psoriasis, rheology, autoimmune pathology. The joints of the joints are affected by the patient, including infectious disease stages including tuberculosis, chlamydia, staphylococci and other infectious diseases.
- Consequences of aggravated forms of respiratory disease - influenza, acute respiratory virus infection, acute respiratory infection;
- Patient weight gain - disproportionate load on tissue joints, sustained mechanical action, resulting in morphological deviations and damage to cartilage structure;
- Excessive hypothermia leads to the destruction of cartilage tissue integrity and the loss of synovial fluid structure;
- Thyroid disease.
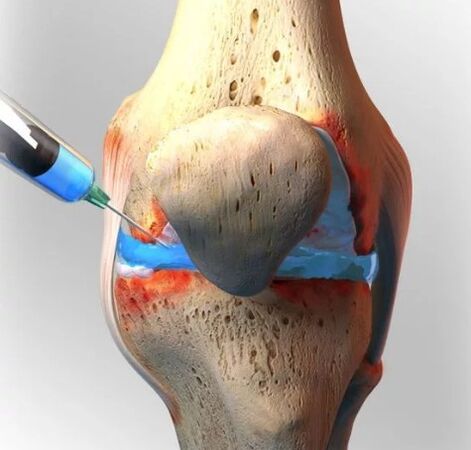
A separate location in the cause of arthritis is a genetic factor. It is genetic abnormalities that can cause abnormal development of joint tissues and physiological functions of collagen fibers, which are responsible for joint flexibility and mobility.
Meanwhile, other concomitant factors are the causes of this pathological development: vitamin deficiency, intoxication or overdose caused by intake quality, the patient's age, pathological processes of blood formation and blood flow, hormone abnormalities and disease disorders.
Mechanisms of disease progression
When joint disease occurs when any cause of joint disease occurs, the pathological process begins to develop. Their progress mechanism has not been fully studied, but the main stages of official medicine are known.
In the initial stage, abnormal changes in the structure and synovial fluid of the cartilage tissue will occur. All these benefits are either taken up by the violation of the metabolic process in which the joint tissue does not receive a sufficient number of necessary components, or are deprived of some of them.
Next, the elasticity of collagen fibers and the flexibility of cartilage are lost because in the body, hyaluronic acid does not have time to produce due to lack of nutrients, which provides the softness and flexibility of the structure composition of the collagen fibers. The cartilage gradually drys, becomes brittle and ruptured. The liquid in the bursa is gradually consumed and then completely disappears.
On the cartilage fabric, a roughness, solid bone tumor forms. At the same time, the deformation and development of other joint tissues, their pathological degeneration, malnutrition and loss of physiological activity.
For patients, these changes mean the occurrence of joint pain, laxity and fixation.
Joint symptoms
Signs of joint articulation are the emergence from the first course, although sometimes they are not so obvious. Characteristics of all stages of arthritis are:

- Pain syndrome;
- The crisp sound when moving;
- inactivity or complete reduction of joint mobility;
- Swelling;
- The conformation of the joint.
pain
Pain usually occurs during exercise. With the intense effort, the feeling of pain intensified and a continued trend was gained. In all types of joints, it hurts anywhere it is localized.
In the initial stage, pain expression is weak, more commonly occurring during the day. Usually, the pain is short-term, still. Pain syndrome develops strongly in both chronic and acute pain forms, more often, with increased performance periods and even troubles when it is still at night.


















































