Ankle arthritis - what is it?
ICD 10 code
reason
- Increased load on joints. Doctors often observe degenerative changes in cartilage and bone tissue in obese patients and professional athletes (football players, bodybuilders, runners, and dancers).
- diabetes.
- Ankle injury.
- Wear uncomfortable shoes and walk in high heels.
- Thyrotoxicosis.
- Tissue dysplasia.
- Injuried.
- Genetic susceptibility.
- fracture.
- Inflammation of joints.
- dislocation.
symptom
- pain. It appears after staying in one location. When a person tries to stand up and lean on his legs, he or she will feel tingling and stiffness of movement. After a few steps, the discomfort will disappear. Pain occurs during and after physical activity.
- The ankle joint makes a clicking or crunching sound when walking.
- Movement restrictions.
- Swelling below the ankle.
- The ligamentous apparatus atrophies and becomes weak.
- Joint deformity (typical of advanced disease).
degree
- First. The degenerative process is just beginning to develop and does not cause much discomfort. The only symptoms were temporary morning stiffness, fatigue and mild pain in the legs. There is a crunching sound when the foot is bent and straightened. No pathological changes were found in X-ray examination. The prognosis with medical treatment is good.
- second. Symptoms of the disease worsen. Morning stiffness will disappear in about an hour. Pain occurs when you first start walking. After only walking a distance of 1 kilometer, people feel that their legs are very tired. When the ankle moves, it makes a crunching sound. X-rays show osteophytes, which are collections at the ends of bones. Surgical treatment is required.
- third. Pain syndrome occurs not only during exercise but also at rest. Without anesthesia, a person cannot work or rest normally. The patient is unable to move independently. X-ray images show cracks, flattening of the joint surface, osteophytes, and subluxation. Treatment options include surgery and medication.
- fourth. Manifestations of this disease are mild. The pain is gone. But stiffness of movement does not allow a person to walk. In stage four, the cartilage has been completely destroyed. X-rays show joint space healing.
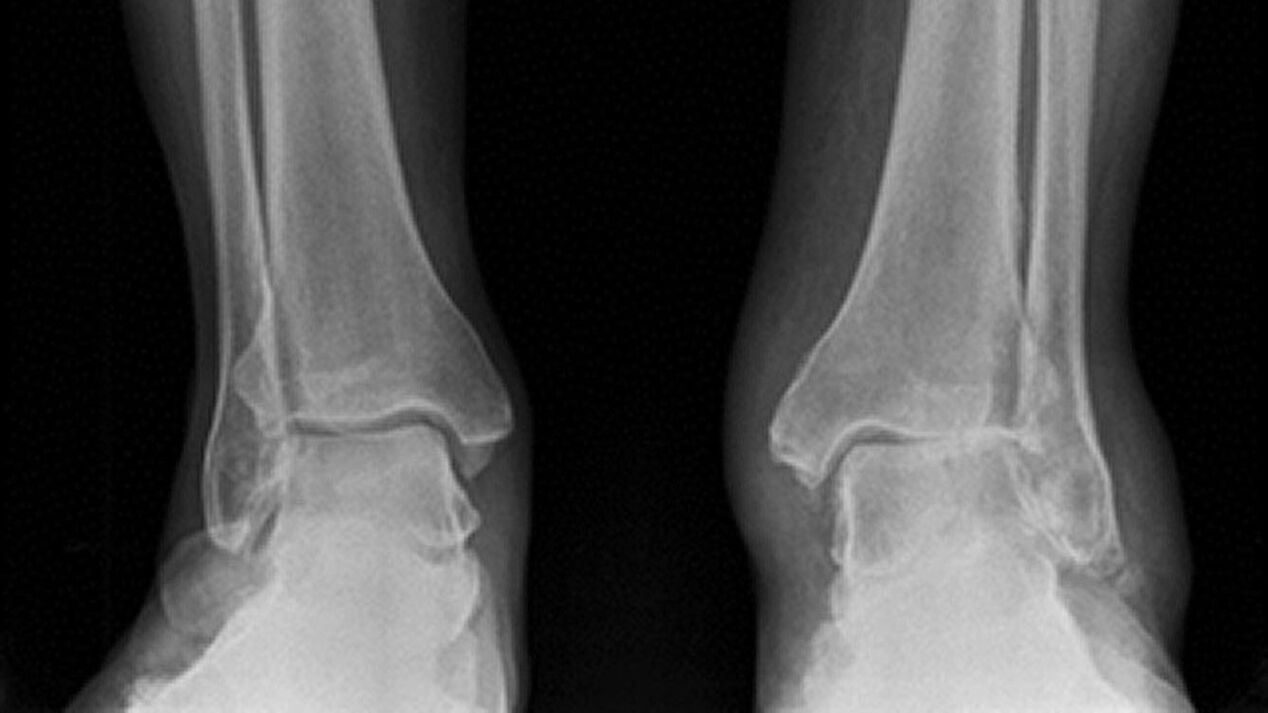
diagnosis
- Blood test (details).
- Rheumatoid test.
- ultrasound.
- CT.
- CRP test.
- Radiography.
- MRI.
treat
- Anti-inflammatory nonsteroidal drugs.
- Chondroprotectant.
- painkiller.
- Corticosteroid hormones.

prevention
- Keep your weight within a normal range.
- Strengthen your spine with special exercises.
- Avoid injury.
- Correct congenital joint structural abnormalities.
- Stop smoking and drinking.
- Prompt treatment of endocrine and vascular diseases.
- If you are genetically predisposed to this disease, get regular preventive tests.


















































