Osteochondrosis is one of the most common pathology of the spine.In this disease, the cartilage tissue of the spine and intervertebral discs is affected.Most of the time, osteochondrosis affects the waist area because it is maximum load when walking, sitting, running, and other activities.
If treatment time does not begin, the disease can lead to discitis, disc hernia, lumbar, Isian, disability.
Development stage
The disease is usually divided into several stages:
- Phase 1- There are minor changes in the intervertebral disc, and the spine is not deformed, and a person will experience slight pain in the lower back.
- Stage 2- Pain in the affected area becomes greater and the invasion of the intervertebral disc becomes more obvious.
- Stage 3- There is a vertebral hernia, spinal deformation.The patient felt severe pain in the affected area.
- Stage 4- It becomes difficult for a person to walk and perform any movement.The pain occurs mild exercise.At this stage, usually, the latter will suffer from disability.
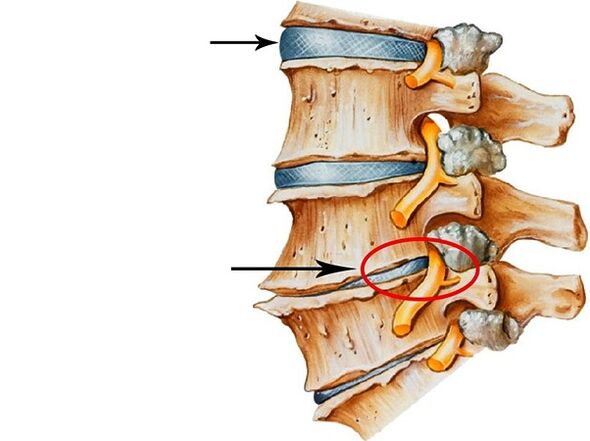
reason
Most commonly, the professional or activity type is associated with physical fatigue and substantial burden in the waist department: builders, porters, utility workers and athletes all suffer from osteocartilage status.Additionally, since they spend most of their time sitting, pathology can occur to teachers, cashiers, office staff.
There are many factors that affect the occurrence of osteochondrosis:
- Lack of physical effort and a sedentary lifestyle.
- Strong loading in the waist area.
- Diseases of joints and spine.
- Lumbar spine injury.
- Flat feet or club feet.
- obesity.
- Poster disease, bent over.
- Scoliosis or meningitis.
- Long-term hypothermia.
- Age-related spinal changes.
- Genetic tendency.
- Some internal diseases of the cardiovascular, nerve, and endocrine system.
- Improper nutrition.
symptom
The main signs of osteochondrosis in the lower back are:
- Strong pain in the lower back, sometimes giving up on the legs and exacerbates when performing any exercise, sneezing, coughing, etc.
- The back muscles are constantly tensioning.
- After staying in the same position for a long time, the back cannot be straightened.
- Unpleasant feeling when tilting or stretching your back.
- Lights on the lower back.
- The sensitivity of the hips, buttocks is lost.
- Chicken skin ump, stinging feeling on the legs.
- Legs and feet numb.
- The constant coldness of the feet and the cold legs.
- Varicocele.
- Violating the effectiveness of a man.
- Women have irregular menstruation.
The main symptom of pathology is pain when you need to consult your doctor urgently.
diagnosis
The diagnosis of osteochondral degeneration begins with a thorough examination of the patient and the collection of tumors - the doctor asks the patient about cases of osteochondralosis in genus, chronic diseases, lifestyle, activity, joint diseases and spine.
In addition, experts have specified tool diagnostic methods, where:
- X-rays in the waist area- Allows you to detect the presence of pathology and the extent of vertebrae damage.
- Computed tomography (CT)- A more accurate research method that allows you to determine the damage to the disc, the degree of change, the degree of spinal deformation.
- MRI- Allows you to thoroughly study the disc, provide information about secondary diseases in the spine, or use in difficult situations, or use with CT or X-rays.
- Bone Marrow Science- A diagnosis in which disc hernia is detected using contrast agent.
Based on the data, experts determine the degree of pathology and specify the necessary treatment methods.
treat
The treatment of osteochondrosis is carried out in full swing.The necessary medications and procedures are prescribed only by the doctor and strictly separate.
First, patients are prescribed many NSAID-based drugs - non-replacement anti-inflammatory drugs that relieve inflammation and eliminate pain in affected areas.Cartilage protectors are also prescribed - drugs that prevent cartilage and feed cartilage tissue destruction process.Vitamins that improve the overall condition of the organism are prescribed as other drugs.
Physical therapy is prescribed for many spinal diseases, including osteochondrosis.The program can enhance blood circulation during lesions, reduce muscle tension, and eliminate pain and inflammation.Osteocartilage, electrophoresis, acupuncture, magnetic therapy and other procedures were prescribed.
The patient also had massages, mud baths or hydrotherapy that relieves muscle tension and fatigue, relaxes and enhances blood flow.A mud bath can eliminate the inflammatory process.
In the first stage of the disease, exercise therapy is prescribed - a color gymnastics whose performance helps restore the spine's mobility to strengthen the muscles in the back.This treatment is not used in stages 3 and 4 of osteochondrosis.
Diet is very important in treating diseases - it must include dietary products rich in minerals - fruits, vegetables, porridge.Be sure to eat low-fat meat because it is rich in protein - eating chicken or turkey is the most useful.Using fermented milk products will be useful.It is recommended to reduce the amount of fat, sharp, smoked, fried vegetables.It is important to observe drinking patterns - make sure to drink at least 1 liter of water per day.
With osteochondrosis in the waist area, treatment in nursing homes will be useful, during which specialists treat the disease throughout the hospital stay in the complex and the patient is constantly supervised by doctors.
If conservative treatments do not help, surgical treatments are used.During operation, the affected wheels or cartilage are replaced by implants.If there is a vertebral hernia, remove it.
prevention
- Limit the load on the lower back.
- Participate in exercise and do morning exercise.
- Eat correctly.
- Try to prevent lumbar spine injuries.
- Avoid hypothermia on the lower back.
- Long seating, change the position of your body more frequently, wake up regularly, have a simple exercise for warmth or just walk.
- Save proper posture and do not bend over.
- If you are doing club-long or flat feet, wear special orthopedic insoles to reduce the load on the spine.


















































