
What is coxarthrosis of the hip?
- primary hip arthropathy. It is considered the most common disease of the hip joint. In the elderly, this pathology manifests itself against the background of age-related changes.
- secondary hip arthropathy. Manifests as a result of any disease.
Causes of Hip Arthropathy
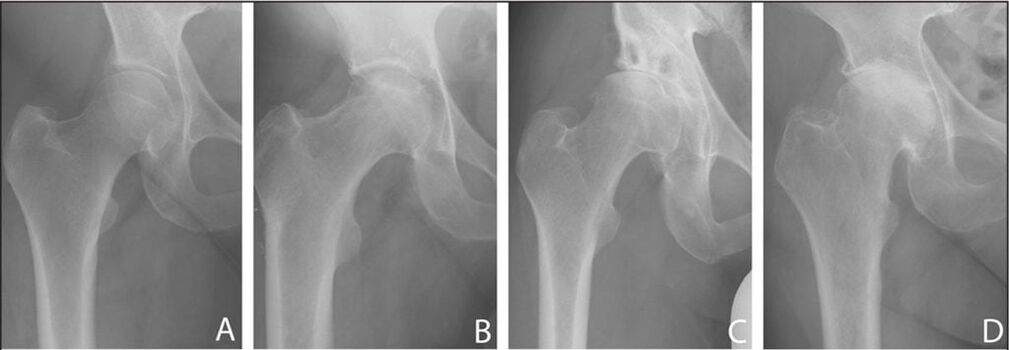
3 stages of development of hip arthropathy
- first. Hip joints at this stage have mild symptoms that are inconsistent and appear in the affected area. At the same time, motor activity is preserved, and for pain relief it is enough to take medications;
- second. When a patient is diagnosed with stage one hip arthritis, the disease does not cause much discomfort, but when it reaches stage two, the symptoms become more pronounced. The pain becomes more severe and begins to radiate to other parts of the body. Significant decrease in exercise capacity, especially after prolonged walking or increased physical exertion;
- third. If second-degree coxaarthrosis is still treatable, in the third stage the pathology becomes chronic. It is accompanied by constant pain that travels to the lower parts of the body. The patient loses the ability to move without crutches. Without appropriate treatment, atrophy of the cartilage and muscle structures can occur.
Types of Hip Arthropathy
- primary hip arthropathy. This pathology manifests in the buttock area and is acquired. In the initial stage, it affects the synovial sac and then moves into the tissue area surrounding the joint. Risk factors include increased pelvic pressure, excessive physical activity, and the presence of inflammatory lesions in the lower limbs and spine. Degenerative lesions are concentrated in tissues that have changed;
- secondary hip arthropathy. This abnormality is hereditary. It is manifested in the joints and musculoskeletal system. After injury in women, and in the context of myelonecrosis of the femoral head, the development of the pathological process may already begin in utero.
- after infection. There are consequences following the identification of an infectious disease;
- post traumatic. Complications following diagnosis of limb injury;
- hormone imbalance. Occurs in the context of metabolic disorders or drug overdose;
- involution. This condition occurs in people over 50 years old due to aging of the body.
diagnostic measures
- radiography. Allows you to study the parameters of the space between cartilages, diagnose the presence of pathological growth and evaluate the condition of the femoral head;
- Ultrasonography. It is possible to track the etiology of changes in bone structure and ligaments, as well as study the dynamics of a patient's condition and determine the extent of the abnormality;
- CT. Enables you to obtain more detailed information about conditions close to joints and tissues;
- MRI. This method provides a detailed picture of the condition of all structures of the hip joint.
Hip arthrosis treatment
- use of drugs;
- physical therapy procedures;
- shockwave therapy;
- physiotherapy.
drug
- NSAIDs. These drugs allow you to achieve a double effect: relieve pain and eliminate the inflammatory process;
- Preparations containing chondroitin, glucosamine and collagen. They allow you to activate the cartilage repair process;
- Steroids. Drugs with strong anti-inflammatory effects. Used when NSAIDs are not effective;
- muscle relaxants. Medications that relieve muscle tone, which are necessary to relieve pain of increasing intensity;
- Means normalization of blood circulationImprove the nutrition of tissues near joints;
- Vitamin B. Complexes containing this vitamin improve neurotransmission, which is especially important when nerve endings are compressed by affected structures.
Gymnastics Treats Hip Arthropathy


physical therapy methods
- UHF;
- laser exposure;
- Ultrasound therapy;
- magnet therapy;
- Exposure to direct current combined with medication;
- paraffin therapy;
- Sonic therapy.
Shock wave therapy for hip joint disease
Surgery
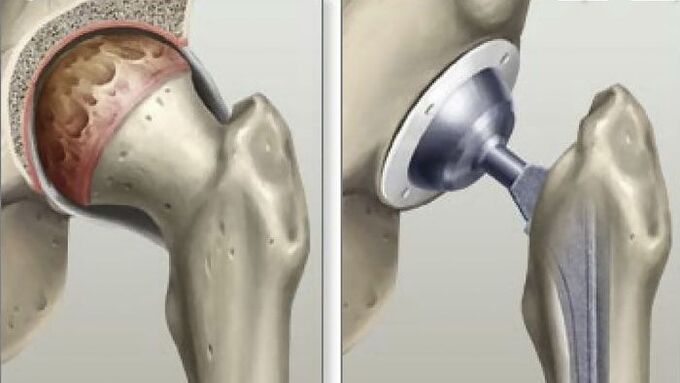
- Increased pain that cannot be relieved by medication;
- Insufficient joint space;
- Violates the integrity of the femoral neck;
- Physical activity is significantly limited.
- Arthrodesis. An intervention that completely immobilizes a joint. For this purpose, special metal plates are used;
- Osteotomy. A surgical procedure involving artificial fracture of the femur to straighten its axis. The resulting parts are placed in optimal positions, which allows you to remove excessive loads from the affected joints;
- Arthroplasty. This is the only method that can restore full function of the hip joint and achieve a complete recovery for the patient. A person can forget about joint problems for 20-30 years after using this method of getting rid of hip joint problems.


















































