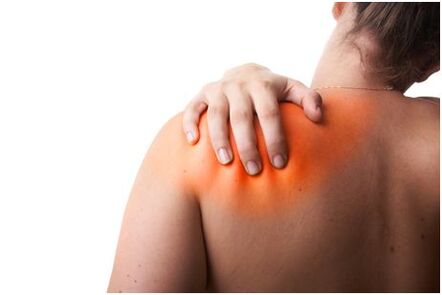
Main causes of shoulder blade and back pain
Injuried
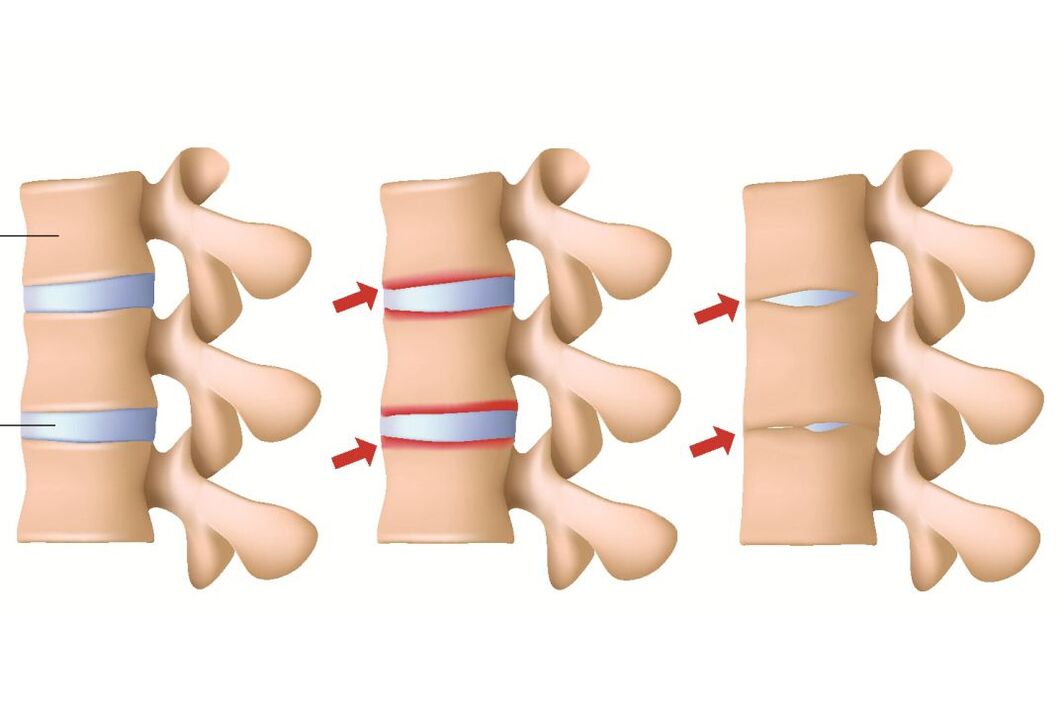
osteochondrosis

scoliosis
Kyphosis
Spondyloarthropathy, spondyloarthritis
Herniation and hernia
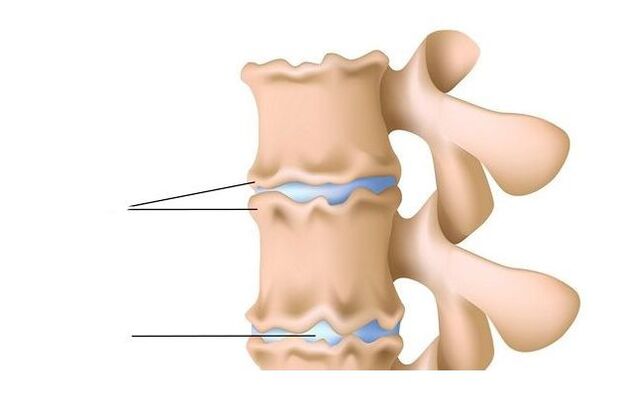
Radiculitis
Humeral periscapular disease
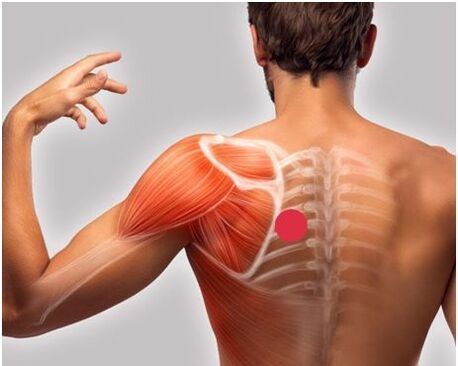
neuralgia
heart disease
gastrointestinal problems
Lung disease
Back pain areas in the shoulder blade area
sternum and shoulder blade pain
Right or left shoulder blade pain
Shoulder blade and neck pain
Types of shoulder blade pain
shoulder blade pain
Shoulder blade pressure pain
Dull pain when breathing in
Throbbing pain in shoulder blades
Shoulder blade pain when moving (walking)
Burning in the shoulder blade area
shoulder pain and nausea
How to Relieve Shoulder Blade Pain

How is shoulder blade pain diagnosed?
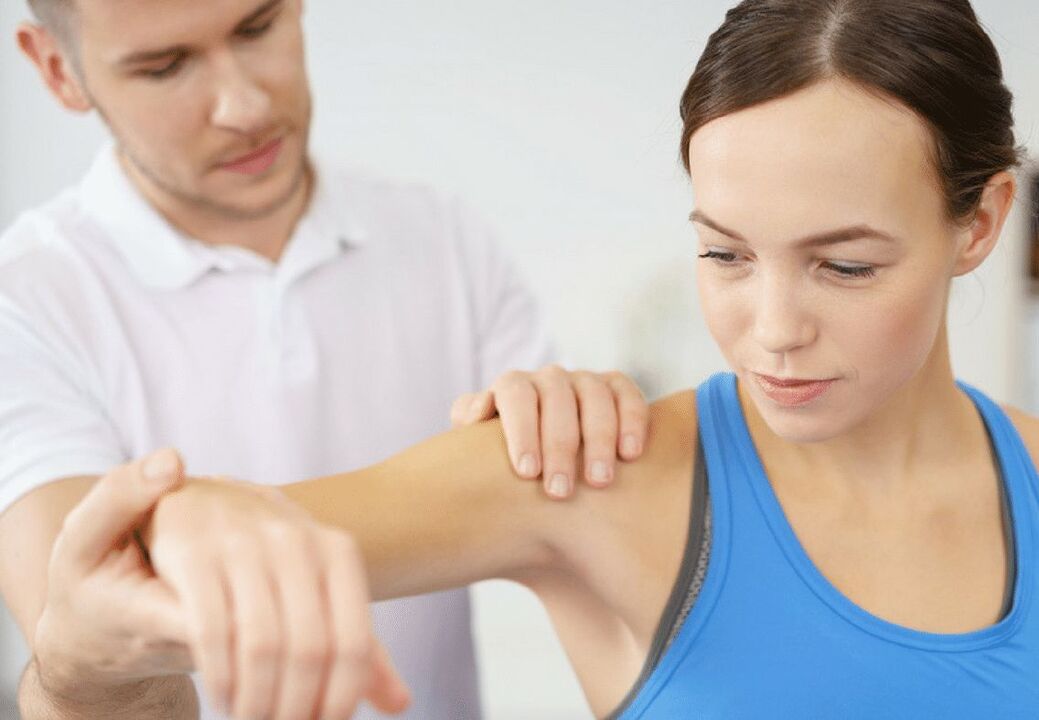

Shoulder Blade Pain Treatment
Treating Shoulder Blade Pain at Home
Which doctor should I consult if I have shoulder blade pain?



















































